

AS9100 is the quality management standard specifically written for the Aerospace and Defense industry. It had long been considered by some entities, such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), that the ISO 9000 series of standards were inadequate in terms of ensuring quality and safety in the “high risk” aerospace industry.
|
|
This course is certified by Probitas Authentication. Successful completion of this course satisfies the Lead Auditor training requirement for AS9100 Aerospace Auditor authentication.
This course prepares you to perform effective Quality Management System (QMS) audits. You’ll learn how to interpret the verbiage of the ISO 9001:2015 & AS9100D Standard and apply it to your own organization. We’ll take you through the full audit process, including: audit planning and preparation, opening meetings, document review, interviewing auditees, closing meetings and reporting. Training includes easy-to-use tools to simplify the auditing process.
This is a practical, how-to course that is not bogged down in academic discussions. We use case studies, role-plays, and other real-life practice exercises to keep the training active and build competence.
| · quality managers | · internal auditors |
| · management representatives | · quality consultants |
| · audit program managers | · top management |
| · lead auditor candidates | · those who perform supplier audits |
None. Our students range from seasoned quality professionals to novices. Our goal is to meet everyone at their current level of competence and increase it, so whether you’re a seasoned professional or are entirely new to quality, you’ll come out of this class a better auditor. All students are required to bring their own printed copy of the AS9100D standard. Most students will be able to obtain a copy from their company.
Agenda |
|
||||||||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 4 |
||||||||||||
|
Activity |
Activity |
|
|||||||||||
|
1 |
Course Introduction |
1 |
Test on TL Unit / Review & Retake |
||||||||||
|
2 |
History of Quality Management |
2 |
Aerospace Industry Unit |
||||||||||
|
3 |
AQMS Objectives Quiz |
3 |
Test on AS Unit / Review & Retake |
||||||||||
|
4 |
In-depth Review of Standard |
4 |
AS9101 Unit |
||||||||||
|
|
Lunch |
5 |
Process-Based Auditing |
||||||||||
|
5 |
Review of Standard (cont’d) |
|
Lunch |
||||||||||
|
6 |
Exercise: Audit Case Studies (part 1) |
6 |
Audit Role Play Exercise 4 |
||||||||||
|
7 |
AS9101 Quiz / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
Day 2 |
8 |
Exercise 3: Closing Meeting |
|||||||||||
|
1 |
Exercise: Audit Case Studies (part 2) |
9 |
Class Wrap-Up |
||||||||||
|
2 |
Learning Game on Pre-assignment |
10 |
Test Prep |
||||||||||
|
3 |
Test on Standard / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
4 |
AU Module – Part 1. Intro to Auditing |
Day 5 |
|||||||||||
|
|
Lunch |
1 |
Test Preparation |
||||||||||
|
5 |
Test on Part 1 / Review & Retake |
2 |
Final Examination |
||||||||||
|
6 |
Part 2. Preparing for an Audit |
||||||||||||
|
7 |
Test on Part 2 / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
8 |
Part 3. Conducting the Audit |
||||||||||||
|
9 |
Test on Part 3 / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
Day 3 |
|||||||||||||
|
1 |
Audit Role Play Exercise 1 |
||||||||||||
|
2 |
Part 4. Completing the Audit |
||||||||||||
|
3 |
Test on Part 4 / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
4 |
Exercise: Writing Audit Findings |
||||||||||||
|
Lunch |
|||||||||||||
|
5 |
Audit Role Play Exercise 2 |
||||||||||||
|
6 |
TL Unit: Leading an Audit Team |
||||||||||||
|
|
This course is certified by Probitas Authentication. Successful completion of this course satisfies the Lead Auditor training requirement for AS9100D Aerospace Auditor authentication.
OverviewThis course prepares you to perform effective Quality Management System (QMS) audits. You’ll learn how to interpret the verbiage of the ISO 9001:2015 & AS9100D Standard and apply its benefits to your own organization. We’ll take you through the full audit process, including: audit planning and preparation, opening meetings, document review, interviewing auditees, closing meetings and reporting. Training includes easy-to-use tools to simplify the auditing process. This is a practical, how-to course that is not bogged down in academic discussions. We use case studies, role-plays, and other real-life practice exercises to keep the training fun and active while building competence. This is the AS9100 Rev D training you’ll actually enjoy. |
 |
| · quality managers | · internal auditors |
| · management representatives | · quality consultants |
| · audit program managers | · top management |
| · lead auditor candidates | · those who perform supplier audits |
None. Our students range from seasoned quality professionals to novices. Our goal is to meet everyone at their current level of competence and increase it, so whether you’re brand new or have been in quality for years, you’ll come out of this class a better auditor. All students are required to bring their own printed copy of the AS9100D standard. Most students will be able to obtain a copy from their company.
Agenda |
|
||||||||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 4 |
||||||||||||
|
Activity |
Activity |
|
|||||||||||
|
1 |
Course Introduction |
1 |
Test on TL Unit / Review & Retake |
||||||||||
|
2 |
History of Quality Management |
2 |
Aerospace Industry Unit |
||||||||||
|
3 |
AQMS Objectives Quiz |
3 |
Test on AS Unit / Review & Retake |
||||||||||
|
4 |
In-depth Review of Standard |
4 |
AS9101 Unit |
||||||||||
|
|
Lunch |
5 |
Process-Based Auditing |
||||||||||
|
5 |
Review of Standard (cont’d) |
|
Lunch |
||||||||||
|
6 |
Exercise: Audit Case Studies (part 1) |
6 |
Audit Role Play Exercise 4 |
||||||||||
|
7 |
AS9101 Quiz / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
Day 2 |
8 |
Exercise 3: Closing Meeting |
|||||||||||
|
1 |
Exercise: Audit Case Studies (part 2) |
9 |
Class Wrap-Up |
||||||||||
|
2 |
Learning Game on Pre-assignment |
10 |
Test Prep |
||||||||||
|
3 |
Test on Standard / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
4 |
AU Module – Part 1. Intro to Auditing |
Day 5 |
|||||||||||
|
|
Lunch |
1 |
Test Preparation |
||||||||||
|
5 |
Test on Part 1 / Review & Retake |
2 |
Final Examination |
||||||||||
|
6 |
Part 2. Preparing for an Audit |
||||||||||||
|
7 |
Test on Part 2 / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
8 |
Part 3. Conducting the Audit |
||||||||||||
|
9 |
Test on Part 3 / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
Day 3 |
|||||||||||||
|
1 |
Audit Role Play Exercise 1 |
||||||||||||
|
2 |
Part 4. Completing the Audit |
||||||||||||
|
3 |
Test on Part 4 / Review & Retake |
||||||||||||
|
4 |
Exercise: Writing Audit Findings |
||||||||||||
|
Lunch |
|||||||||||||
|
5 |
Audit Role Play Exercise 2 |
||||||||||||
|
6 |
TL Unit: Leading an Audit Team |
||||||||||||
Days: 3
7:30 AM- 4:30 PM MST
The AS13100 AESQ (Aerospace Engine Supplier Quality) Supplemental QMS Requirements simplifies and harmonizes: a) the aerospace engine manufacturer requirements for its supply chain, and, b) requirements flowed-down to the engine manufacturers by regulators, customers, and industry. Suppliers with multiple customers will learn how coordinate and apply AS13100 to minimize total requirements and improve overall product quality.
This course provides review of and insight into each of the AESQ supplemental requirements. Workshop activities have been tailored for understanding how to apply this Standard and the additional RM (Reference Manual) requirements. Participants will learn how to apply this Standard within their own organization and coordinate the requirements between their Customers, Regulatory Authorities, and their own Supply Chain.
AESQ AS9100 Supplemental Requirements for – Strategic Planning, Top Management, Competence & Awareness, Risk Management, Monitoring Equipment, Human Factors, Design & Development, Supply Chain Management & Control, Manufacturing Systems, Internal Audits, and Corrective Action
AESQ AS9145 Supplemental Requirements for: APQP – Project Management, Design & Development, Process Design & Development, Validation of Products and Processes; PPAP – File Submission and Disposition, Supply Chain PPAP
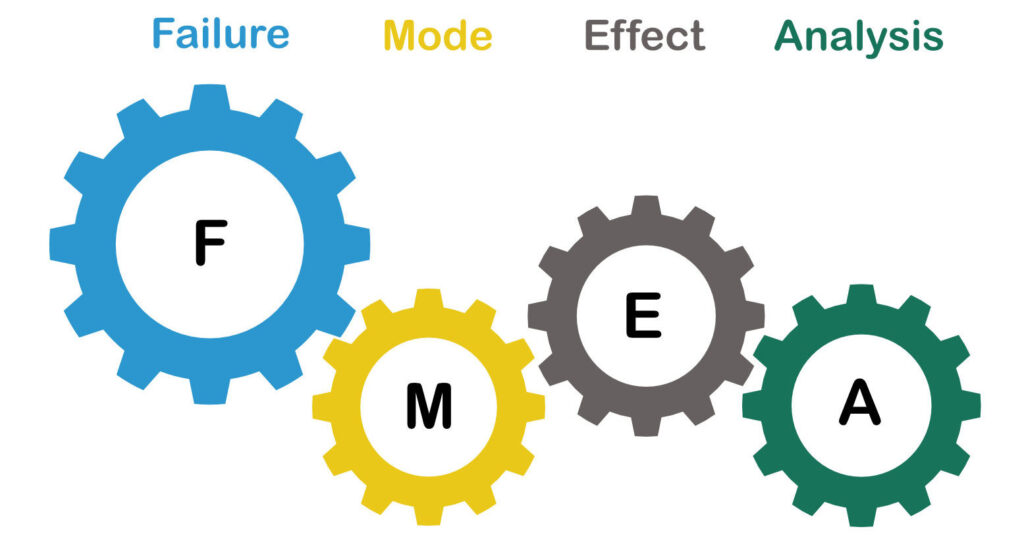
AESQ Core Defect Prevention Quality Tools: DFMEA, PFMEA, Key Characteristics, Process Flow Diagrams, Control Plans, MSA, Capability Studies
Day 1
| Part 1 | Introductions | |
| Part 2 | History, Purpose, Related Publications (SAE/AESQ/ISO and Other), Terms and Definitions, Standards/Handbooks/Manuals | |
| Activity #1: Terminology | ||
| Part 3 | Detailed Review of the AS13100 additional requirements to the AS9100 standard: Clauses 1-8.3 | |
| Topics & In-Class Exercises: Supplier Type and Supplemental Requirements & Appendix B; AS9115 Applicability; Compliance Assessment; Human Factors RM 13010; ISO 31000 Risk Management; RM 13003 MSA; MSA Acceptance Limits; Auditor Qualifications – Training; Delegations of Product Release Verification; Retention of Documented Information; Prevention of Counterfeit Parts AS 6174; APQP & PPAP in Design; Design FMEA Process; AS9146 FOD; Design Phases RM 13008; Design for ‘X’ (DfX: DfM, DfA, DfS, DfC); Critical Items & Key Characteristics; | ||
| Activity #2: MSA Repeatability Mitigation RM 13003
Activity #3a: Design FMEA RM 13004 |
||
| Estimated time for day 1 | 7.5 hours in class |
Day 2
| Part 3 Cont. | Detailed Review of the AS13100 additional requirements to the AS9100 standard: Clauses 8.4 – 10 | |
| Topics & In-Class Exercises: Sub-tier Assessment Process (SCMH); Audit Types RM 13005; ITAR/EAR; D&D Software Requirements Specification (SCMH); Process FMEA; PFMEA/Control Plan process RM 13004; AS9102 FAI; Rework & Repair of NC Product RM 13011; Process Control Methods RM 13006; Process Capability Cp, Pp, Cpk, RM 13006; Alternate Inspection Frequency Plans RM 13002; Appendix C Training Syllabus Process Controls RM 13006; Internal Audit Types & Frequencies; Quality Audits – Production Process over 3-years RM 13005; 8D Structured Problem Solving RM 13000; Human Factors in Problem Solving RM 13010; Lean Six Sigma & 5S; AS 9145 2016-11 & APQP Process Flow; | ||
| Activity #3b: Process FMEA RM 13004
Activity #4: 8D Problem Solving Case Study |
||
| Part 4 | AS13100 Chapter B AS9145 Supplemental Requirements | |
| Topics & In-Class Exercises: APQP and PPAP Process Flow Diagram; APQP & PPAP Timing Chart & Events; DFMEA RM 13004; Process Flow Diagram RM 13004; Control Plan RM 13004; Production Preparation Plan AS 13100; Alternate Inspection Plan RM 13002 | ||
| Estimated time for day 2 | 7.5 hours in class | |
| Day 3 | ||
| Part 4 cont. | AS13100 Chapter B AS9145 Supplemental Requirements cont. | |
| Topics & In-Class Exercises: Pre-Launch Control Plan RM 1345; MSA GRR RM 13003; AESQ PPAP Elements AS13100; PPAP Coordinator and CAR3 Training RM 12145; PPAP Submission/Retention Levels; PPAP Elements and RM References AS13100; Typical Use of PPAP Elements RM 13145; Supply Chain Risk Management RM 13145; APQP Assurance Actions AS13100; Robust Statistical Evaluations Chart RM 13006; | ||
| Part 5 | Core Defect Prevention Quality Tools APQP & PPAP | |
| Topics & In-Class Exercises: APQP Phase 1-5 Resource Manuals References; Design FMEA Severity/Occurrence/Detection Ranking Tables RM 13004; DFMEA Potential Causes & Controls RM 13004; Critical Items, Key Characteristics, Special Requirements AS9100; Process Flow Diagram, Defect Detection RM 13004; PFMEA Severity, Occurrence, Detection Rating Tables RM 13004; Control Plan Inputs/Defect Detection RM 13004; Cp and Cpk Calculations | ||
| Activity #5: Use of PPAP Submissions in Supplier Control RM 13145 | ||
| Estimated Time for Day 3 | 7.5 hours | |
Days: 3 • CEU Hrs: 2.4
Time: 7:30 a.m.- 6:30 p.m. MST
Audience: Beginner to Advanced
This course prepares you to perform internal QMS audits using industry-proven techniques and to apply the proper interpretation of the ISO standard to real-life audit situations. You’ll follow the full audit process including: audit tools and preparation, opening meetings, audit interviews, closing meetings, and reporting. This is a very practical class that is not “bogged-down” with academic discussions of quality topics that have limited utility for class attendees.
This Internal Audit class makes extensive use of activities and case studies to help you fully understand the requirements of quality system auditing to the AS9100:2016 Rev D standard. Since people “lock” new understanding into long-term memory much better when they apply it, lecture time is held to a minimum providing you time to grasp and then practice your newly acquired skills in simulated real-life audit situations.

Individuals who will perform audits to AS9100:2016 Rev D Standards or Quality Management Systems, individuals assisting their organizations toward AS9100:2016 Rev D registration, or individuals who are frequently audited should attend this training. Quality directors, managers, engineers, auditors, ISO coordinators, laboratory quality professionals, and anyone engaged in quality audits will benefit from this training.
There are no required prerequisites. This course is routinely taught to quality novices and lifetime professionals. All attendees are required to bring their own copy of the AS9100:2016 Rev D Quality Management Standard Requirements for this training course. These will not be provided for you. We strongly advise you bring a “paper” copy.
Part 1: Introductions and Self-Assessment
Part 2: Quality Terminology and Definitions
Part 3: Requirements of AS9100:2009
Part 4: The Audit Process: Roles and Duties
Part 5: The Audit Process: Performing the Audit Process
Part 6: The Audit Process: Audit Skills and Techniques
Part 7: The Audit Process: Finalizing the Audit
Review and Examination of Certificate
Days: 3 • CEU Hrs: 2.4
Time: 7:30 a.m.- 5:30 p.m.
Audience: Beginner to Advanced
This course prepares you to perform internal QMS audits using industry-proven techniques and to apply the proper interpretation of the ISO standard to real-life audit situations. You’ll follow the full audit process including: audit tools and preparation, opening meetings, audit interviews, closing meetings, and reporting. This is a very practical class that is not “bogged-down” with academic discussions of quality topics that have limited utility for class attendees.
This Internal Audit class makes extensive use of activities and case studies to help you fully understand the requirements of quality system auditing to the AS9100:2016 Rev D standard. Since people “lock” new understanding into long-term memory much better when they apply it, lecture time is held to a minimum providing you time to grasp and then practice your newly acquired skills in simulated real-life audit situations.

Individuals who will perform audits to AS9100:2016 Rev D Standards or Quality Management Systems, individuals assisting their organizations toward AS9100:2016 Rev D registration, or individuals who are frequently audited should attend this training. Quality directors, managers, engineers, auditors, ISO coordinators, laboratory quality professionals, and anyone engaged in quality audits will benefit from this training.
There are no required prerequisites. This course is routinely taught to quality novices and lifetime professionals. All attendees are required to bring their own copy of the AS9100:2016 Rev D Quality Management Standard Requirements for this training course. These will not be provided for you. We strongly advise you bring a “paper” copy.
Part 1: Introductions and Self-Assessment
Part 2: Quality Terminology and Definitions
Part 3: Requirements of AS9100:2009
Part 4: The Audit Process: Roles and Duties
Part 5: The Audit Process: Performing the Audit Process
Part 6: The Audit Process: Audit Skills and Techniques
Part 7: The Audit Process: Finalizing the Audit
Review and Examination of Certificate
Days: 2
Time: 7:30 AM- 4:30 PM MST
AXEON’s training courses begin with your objectives in mind. Before any training begins the instructor must have an objective to deliver your desired outcome. If the course does not have a specific objective, students can go through the motions with little added value. AXEON’s course setup begins with a candid discussion of your needs and expectations with the course instructor to develop specific areas of focus for the class. Below is a general outline for the course and topics that will be covered.
Statistical process control (SPC) procedures help you monitor process behavior. One of the staple SPC tools used by quality process analysts, improvement associates, inspectors and more is the control chart. Axeon’s statistical process control training will walk you through the details of control charting and other SPC procedures and how to apply them within your organization.
| · Quality & Process Engineers | · Process Development & Validation Personnel |
| · Quality Technicians | · Manufacturing/Operations Personnel |
| · Production Supervisors | · Process Improvement Personnel |
| · SPC Supervisors | · Supplier Quality Personnel |
| · Laboratory Personnel | · Six Sigma Professionals |
Days: 2
7:30 AM- 4:30 PM MST
This class teaches participants the Aerospace Risk Requirements (per AS9100, 9110, and 9120) as well as the specific requirements for Operation Risk as defined in AS13004 PFMEA and Control Plans. The course follows a well-organized, systematic approach to Identify, Assess, and Mitigate Risks that impact Aerospace organizations and the risks to their customers and stakeholders. While Risk Management is a basic requirement of ISO 9001, the Aerospace standards incorporate all of these requirements and add further requirements to make aerospace products and services safe and effective throughout the Supply Chain. Further, with reduced risks inherent in the Design and Manufacture of aerospace articles, the costs associated with their manufacture should be reduced.
Who Should Attend
|
 |

Days: 2 • CEU Hrs: 1.9
Time: 7:30 a.m.- 4:30 p.m. MST
Audience: Beginner to Advanced
This course prepares you to perform internal QMS audits using industry-proven techniques and to apply proper interpretation of the ISO standard to real life audit situations. You’ll follow the full audit process including: audit tools and preparation, opening meetings, audit interviews, closing meetings, and reporting. This is a very practical class that is not “bogged-down” with academic discussions of quality topics that have limited utility for class attendees.
This Internal Audit class makes extensive use of activities and case studies to help you fully understand the requirements of quality system auditing to the AS9100:2016 standard. Since people “lock” new understanding into long-term memory much better when they apply it, lecture time is held to a minimum providing you time to grasp and then practice your newly acquired skills in simulated real-life audit situations.
Who Should Attend?Individuals who will perform audits to the AS9100:2016 or ISO 9001:2015 Standards or Quality Management Systems, individuals assisting their organizations toward AS9100:2016 registration, or individuals who are frequently audited should attend this training. Quality directors, managers, engineers, auditors, ISO coordinators, laboratory quality professionals, and anyone engaged in quality audits will benefit from this training. |
 |
There are no required prerequisites. This course is routinely taught to quality novices and life-time professionals. All attendees are required to bring their own copy of the AS9100:2016 Quality Management Standard Requirements to this training course. These will not be provided for you. We strongly advise you bring a “paper” copy.
Part 1: Introductions and Self-Assessment
Part 2: Quality Terminology and Definitions
Part 3: Requirements of AS9100:2009
Part 4: The Audit Process: Roles and Duties
Part 5: The Audit Process: Performing the Audit Process
Part 6: The Audit Process: Audit Skills and Techniques
Part 7: The Audit Process: Finalizing the Audit
Review and Examination of Certificate
Days: 2
Time: 7:30 AM- 4:30 PM MST
Audience: Beginner to Advanced
Human Factors is a term that appears in the latest versions of several ISO standards, including:
This Human Factors online training helps you to understand human factors in the context of each standard. You will learn how to apply the concept of human factors to your management system and address the standard requirements. You will also receive practical tools, proven methodologies, and helpful tips to make the job easier for you.
As with all of Axeon’s courses, this is a practical, how-to that is not bogged down in academic discussions. We use case studies, practice exercises, and learning activities to keep the training activities and build competence.
| · Quality managers | Also: |
| · Management representatives | · Quality consultants |
| · Quality engineers | · Those involved in performing corrective actions |
| · Safety managers | · Those involved in medical device risk management |
| · Top management | · Preparation Of Checklists From Process Analysis |
| · Regulatory affairs specialists | |
Prerequisites
None. Our students range from seasoned quality professionals to novices. Our goal is to meet everyone at their current level of competence and increase it.
Intro to Human Factors
Review ISO Standard Requirements: 9001, AS9100D, 14971, 45001
Definitions of Human Factors by Standard
Human Factors and Root Cause Analysis
Corrective Action and Human Factors
The 13 Most Common Human Factors
Activity: Applying Human Factors in Corrective Action
Human Factors and Poka-Yoke
Definition & History of Poka-Yoke
Methodology for Poka-Yoke
Activity: Applying Poka-Yoke to Human Factors
Human Factors and Health & Safety
Definition of Human Factors in Health & Safety
Human Factors and Ergonomics
How Human Factors influence Safety at Work
Activity: Applying Human Factors to Safety
Human Factors and Medical Devices
Methodology for Considering Human Factors in Risk Assessment
Device Design According to Human Factors Consideration
Human Factors in Post-Market Surveillance
Final Test
Days: 2
Time: 7:30 AM – 4:30 PM MST
This standard establishes requirements for performing and documenting APQP and PPAP. APQP begins with conceptual product needs and extends through product definition, production planning, product and process validation (i.e., PPAP), product use, and post-delivery service. This standard integrates and collaborates with the requirements of the 9100, 9102, 9103, and 9110 standards.
The requirements specified in this standard are complementary (not alternative) to contractual and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements. Should there be a conflict between the requirements of this standard and applicable statutory or regulatory requirements, the latter shall take precedence.
Learning Objectives
|
 |
Any others involved in the auditing or implementation of Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) activities including Control Plans.
| 1 | Introduction |
| 2 | History, Aerospace requirements for APQP/PPAP |
| 3 | Activity #1 Terminology |
| 4 | AS9145 Clause 4.1 – 4.2 General Requirements, Start-Up |
| 5 | Workshop #1 SCMH Checklists |
| 6 | AS9145 Clause 4.3 Phase I Planning |
| 7 | Workshop #2 |
| 8 | AS9145 Clause 4.4 Phase 2 Product Design & Development |
| 9 | Workshop #3 |
| 10 | AS9145 Clause 4.5 Phase 3 Process Design & Development |
| Day 1 | |
| Day 2 | |
| 1 | AS9145 Clause 4.5 Phase 3 Process Design & Development |
| 2 | Workshop #4 |
| 3 | AS9145 Clause 4.6 Phase 4 Product & Process Validation |
| 4 | AS9145 Clause 4.7 Phase 5 Ongoing Production, Use, Post Delivery |
| 5 | Workshop #5 |
| 6 | AS9145 Clause 5.1 – 5.4 PPAP |
| 7 | Workshop #6 |
| 8 | In-Class Case Study |
Days: 2
Time: 7:30 a.m.- 4:30 p.m. MST
As Root Cause CAPA for Aerospace, an AS13000 training is a must-have. If you are a Boeing, Airbus, or other top OEM supplier, you need this class! All suppliers for the top OEM’s are required to have an 8D Practitioner. This course fulfills the training and testing requirements to become an 8D Practitioner.
AS13000 defines the Problem-Solving standard for suppliers within the aero-engine sector, with the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving method being the basis for this standard.
| This 2-day course provides students with a comprehensive and standardized set of tools to become an 8D practitioner and meets all the requirements of “training syllabus” (see AS1300 APPENDIX C). Successful application of 8D achieves robust corrective and preventive actions to reduce the risk of repeat occurrences and minimize the cost of poor quality. This is essential to enable long-term customer-supplier relationships and positively contributes towards zero defects and customer satisfaction.
This course includes the practical application of each of the 8D disciplines. |
 |
 |
Learning Objectives:
|
An AS13000 training is a requirement for Aerospace Suppliers of any top OEM. Any employees that will conduct a corrective action or participate as a team member, as well as any individual who would like to gain an in depth understanding of the 8-D process.
Days: 1
Time: Day 1 7:30 a.m.- 4:30 p.m.
Audience: Beginner to Advanced
This course introduces you to the Nadcap process and helps you get prepared for the certification process including the onsite assessment performed by the Nadcap auditor. You’ll learn about Nadcap and how to effectively work within the Nadcap system.
Individuals responsible for obtaining or maintaining Nadcap accreditation for their organizations. Quality directors, managers, process owners, quality engineers, auditors, laboratory personnel, and production management.
Prerequisites
There are no required prerequisites. This course is routinely taught to quality novices and life-time professionals.
Days: 1
Time: 7:30 AM-4:30 PM MST
Audience: Top management
A QMS (Quality Management System) is NOT a cost of doing business. It’s an investment. And top management should expect to get a financial return on that investment. However, the Return On Investment (ROI) they receive will be greatly impacted by the level of leadership and commitment they provide concerning the management system.
The newest versions of most ISO management standards have amplified the requirements for top management, in accordance with ISO 9001:2015. In this highly interactive course, senior managers will learn how to fulfill their new responsibilities, take accountability, and maximize the ROI they get from their management systems.
This class will help to show the true value of your quality management system and how much it really adds to your bottom line. It will also help your company to increase the ROI of your QMS.
If you want to improve your company’s bottom line or show your boss how much your QMS is already contributing to profits then this class is for you.
Benefits of a Quality Management System
Overview of Quality Principles
How to Maximize the ROI from your QMS
The Five Biggest Mistakes Executives Make with Quality Management
Final Test
Days: 1
Time: 7:30a.m.-4:30p.m. MST
ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) and the EAR (Export Administration Regulations) are export control regulations run by different departments of the US Government. Both of them are designed to help ensure that defense-related technology does not get into the wrong hands. An export license is a general term for both ITAR and EAR-controlled items in which the US Government has granted permission to transport or sell potentially dangerous items to foreign countries or parties.
To be ITAR or EAR compliant, a manufacturer or exporter whose articles or services appear on the USML or CCL lists must register with the U.S. State Department’s Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC). ITAR and EAR compliance can be problematic for a global corporation because the data related to a specific type of technology may need to be transferred over the Internet or stored locally outside the United States to make business processes flow smoothly. It is the responsibility of the manufacturer or exporter to take the necessary steps to certify that they are in compliance with the regulations.
Export control laws provide for substantial penalties, both civil and criminal. Failure to comply with ITAR can result in civil fines as high as $500,000 per violation, while criminal penalties include fines of up to $1,000,000 and 10 years imprisonment per violation. Under EAR, maximum civil fines can reach $250,000 per violation. Criminal penalties can be as high as $1,000,000 and 20 years imprisonment per violation.
The Department of State is responsible for the export and temporary import of defense articles and services governed by 22 U.S.C. 2778 of the Arms Export Control Act and Executive Order 13637. The International Traffic in Arms Regulations (“ITAR,” 22 CFR 120-130) implements the AECA.
The more stringent of the two sets of regulations was written for articles with direct defense-related applications. Articles specifically designed or otherwise intended for military end-use are enumerated on the United States Munitions List (USML) or the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) Annex and therefore controlled by International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) which is administered by the Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) at the State Department. Items, services, and information are all covered by the ITAR regulations. The most controlled items are Significant Military Equipment (SME) which have “capacity for substantial military utility or capability” such as tanks, high explosives, naval vessels, attack helicopters, etc which are noted on the USML with an asterisk. Some examples include; an export license (DSP-5), exchanging technical emails or teaching how to repair an ITAR-covered item which requires a Technical Assistance Agreement (TAA), and allowing a foreign company to manufacture an item requires a Manufacturing License Agreement (MLA).
Most other items not specifically listed in the USML, but with the capability to be used for either civilian or military purposes are considered “dual-use” and controlled under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) which is administered by the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) at the Department of Commerce (DoC). The Commerce Control List (CCL) is the equivalent list at the DoC to the State Department’s USML. The CCL specifically controls for Chemical & Biological Weapons, Nuclear Nonproliferation, National Security, Missile Technology, Regional Stability, Firearm Convention, Crime Control, and Anti-Terrorism. The level of control depends on the country being exported to, destination party, end-use, and Export Control Classification Number (ECCN). Specifically, there are “600 Series” and “500 Series” items that are more strictly controlled than the rest of the CCL, but less strictly controlled than the articles on the USML.
This introductory course is for business executives, international contracting specialists, contract managers and administrators, program and project managers, marketing professionals, engineers, and other technical personnel, newly appointed export compliance officers, logistics personnel, and legal and financial advisors.
Days: 1 • CEU Hrs: 0.8
Time: 7:30 AM- 4:30 PM MST
Audience: Beginner to Advanced
The aviation, space, and defense industry established the International Aerospace Quality Group (IAQG). The IAQG strives to improve quality and safety while reducing cost throughout the value stream. The AS9102 Rev C First Article Inspection standard applies to the complete value stream.
The FAI process requirements are used at all levels of the supply chain by organizations around the world. This standard provides a consistent process and documentation requirements for verification of aviation, space, and defense product.
Its use should result in improved: a) quality, b) schedule, and c) cost performance by: the reduction or elimination of organization-unique requirements and wider application of good practices.
There are no required prerequisites. This course is routinely taught to quality novices and life-time professionals. All attendees are required to bring their own copy of the AS9102 standard. These will not be provided for you. We strongly advise you bring a “paper” copy.
Learn what AS9100 registration means for your organization and how to implement it to your AS9100 Rev D QMS to gain a competitive advantage.
Many organizations are introduced to management systems because they are forced to consider ISO certification. This overview shows how system development can happen in many different ways, but the best approach is to investigate your existing processes and system and align them with your business objectives.
As leaders, Top Managers need to be stakeholders in the achievement of the Quality Management System, accountable for its effectiveness and engage the company in achieving the intended results of the QMS- among other requirements. Every organization is different, so we customize every executive overview to incorporate top management’s particular learning and system development objectives.
Who should attend?
You will learn:
Days: 1
7:30 AM- 4:30 PM MST
Manufacturing Management System, Design Analysis for Manufacturing, Manufacturing: Feasibility, Risk, Readiness Levels, Manufacturing Planning, Materials Management, Manufacturing Workforce, Tooling/Test Equipment/Facilities, MSA, Process Capabilities, FAI, and Supplier Quality and Management
The AS6500 standard is applicable to all phases of the system acquisition life cycle. It is intended for use on all programs with manufacturing content. It requires proven manufacturing management practices with the goal of delivering affordable and capable systems to the extent that it is invoked contractually. The agreement between the customer and the organization shall include the manufacturing management requirements in AS6500 based upon tailoring the requirements of this standard to address the program situation.
Many international publications are referenced within this 16-page standard to give additional insight in meeting customer requirements and enhancing the performance of your current Manufacturing Management System.
Day 1
| Part 1 | Introductions |
| Part 2 | History, Purpose, Terms and Definitions |
| Activity #1A & 1B: Terminology | |
| Part 3 | Detailed Review of the AS6500 Standard Requirements |
| Topics & In-Class Exercises: MS Objectives, Producibility Analysis: Trade Curves, Design for Manufacturing and Assembly, MIL HDBK 727, Key and Critical Characteristics: Process Flow and Control Plans; PFMEA: Activity #3 PFMEA, Manufacturing Feasibility, MRLs, Production Readiness, Materials Management DMSMS, SD-22, Cost, Manufacturing Modeling/Simulations; Manufacturing System Verification, Lean Manufacturing, MSA, LOB, Lean/Six Sigma, VR, AS9103, Cp and Cpk Process Capability, Activity #4: Cp and Cpk, FAI/FAT Supplier Management and Quality: PPAP | |
| Activity #2: Management System Objectives Activity #3: Process Flow Diagram and PFMEA Activity #4: Calculate Cp and Cpk (Process Capability) |
Days: 1 • CEU Hrs: 4.8
Time: 7:30 a.m.- 4:30 p.m. MST
Audience: Beginner to Advanced